
School system & compulsory education
Germany is known worldwide for its education system. Here you can find out more about the German school system.
Germany's school system
Your children need to attend school from the age of six, as school attendance is compulsory in Germany. The majority of schools in Germany are run by the state and offer free education. You also have the option of sending your children to fee-paying private and international schools. Home education is only allowed in exceptional cases, such as when children are ill and unable to attend school for a prolonged period. As a parent, you will receive an invitation from the relevant school authority with details of the exact dates and registration procedures. You can also obtain information on compulsory school attendance from the competent Ministry of Education.
Education policy is the responsibility of Germany’s federal states. Searching the websites of the ministries in the relevant federal state is therefore the most effective way of finding a suitable school for your child. You can filter by region, school type and internationality. For more information about specialisations, all-day education and how to register, please visit the schools’ own websites.
School search
This means that the school system will depend to some extent on the region to which you and your family move. Children do not always follow exactly the same curriculum in all federal states, and teaching materials may also differ.
Qualifications are recognized nationwide
However, the comparability of qualifications and the eligibility for admission to higher education in Germany is guaranteed in all federal states. This is reassuring if you have to move to another federal state for work.
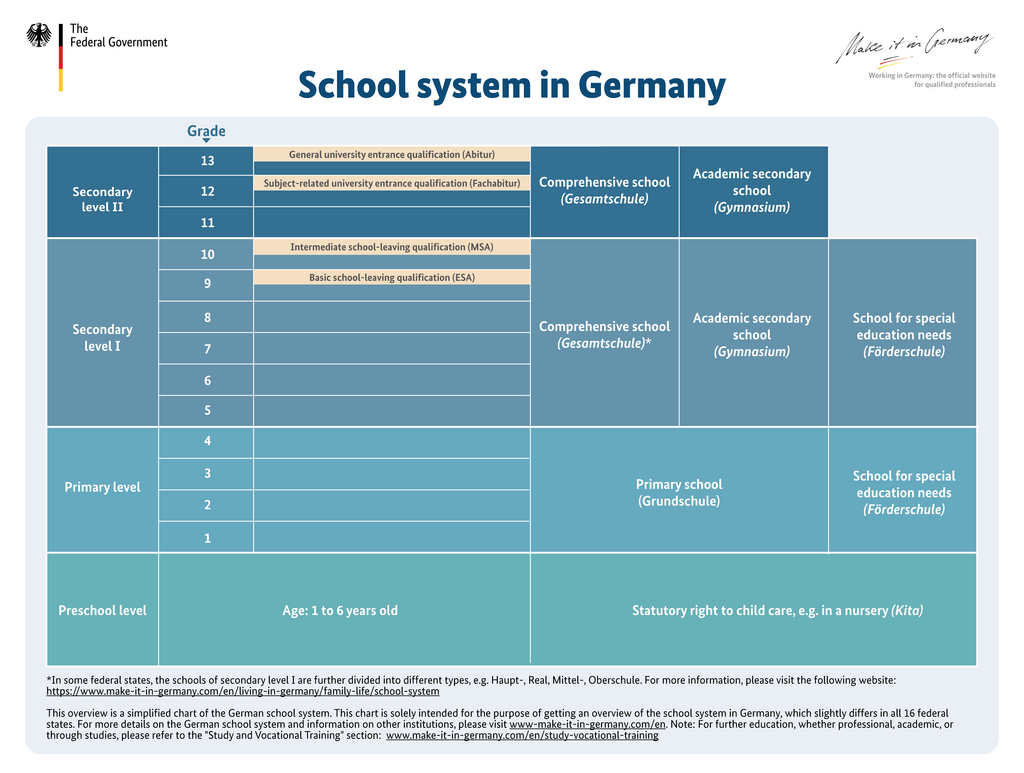
The types of school also vary from state to state. In general, however, the German school system is structured as follows:
Primary school (Grundschule)
Children usually start primary school at the age of six, and attend from the first to the fourth grade. In Berlin and Brandenburg only, primary school does not end until the sixth grade. At the end of primary school, you and your child’s teachers will decide which type of secondary school your child will attend from the fifth (or seventh) grade, based on your child’s academic performance. The following classification is most commonly used for secondary education:
- Primary school (Grundschule) (grades 1-4/6)
- Comprehensive school (Gesamtschule or Gemeinschaftsschule) (grades 5/7–9/10 or 12/13)
- Grammar school (Gymnasium) (grades 5/7–12/13)
Comprehensive school (Gesamtschule/Gemeinschaftsschule)
Depending on their academic performance and the number of years of schooling they have completed, students can obtain the first school-leaving certificate (Hauptschulabschluss), a lower secondary school-leaving certificate (Realschulabschluss, Mittlere Reife), an entrance qualification for universities of applied sciences (Fachhochschulreife) or a general higher education entrance qualification (Abitur). In some federal states, these schools have special names such as Mittelschule, Sekundarschule, Oberschule, etc., but they all function in a similar way. A few federal states also still have Hauptschulen and Realschulen.
After obtaining one of the qualifications at lower secondary level (Sekundarstufe I), students have the option of continuing to attend general schooling, e.g. to take the Abitur, or of taking vocational education and vocational training (VET); Vocational training can be either school-based or dual (school + work-based training).
Students must complete nine or ten years of full-time education (depending on the federal state) and two or three years of part-time education, or until they reach the age of 18. The requirement to be in part-time education is met if, after completing general education (full-time schooling), students are in vocational training, for example, which involves attending a vocational school (dual education).
Grammar school (Gymnasium)
After completing the twelfth or thirteenth grade (depending on the federal state) and successfully passing the final examination, students receive the Abitur or Fachabitur. This qualification then enables them to study at a higher education institution, such as university or a university of applied sciences, respectively. Students who have completed grammar school also have the option of going straight into the world of work by pursuing vocational training.
Germany's education system
School enrolment of children and teenagers newly arrived from abroad
If your children are of school age when entering Germany, you will no doubt be wondering how they can be found a place in a school. This is decided by the school management in consultation with the local education authority. As a general rule, children who have recently entered the country are not able to attend regular school lessons and will be offered special trial lessons instead due to their lack of German skills. The goal is to integrate them as soon as possible into regular school classes.
How to recognise a good school
As a rule, you are free to decide which school your child should attend. It is therefore a good idea to take a look at a few schools. One sign of a good school is that it not only provides high-quality instruction, but also offers extracurricular activities such as theatre, sports, language and music clubs, and school trips. A good school also encourages parent involvement. In addition to finding out whether the school has a place for your child, you should also ask about extracurricular options. If your children are not yet fluent in German, make sure that the school offers German classes, usually referred to as Deutsch als Zweitsprache (German as a foreign language). Here the teachers will make sure that your child understands the lessons and can keep up with the curriculum.
Information on the web
- Association of German International Schools Federation of international schools in Germany
- Standing Conference of the Ministers of Education and Cultural Affairs of the Federal States (KMK) Germany’s school system
- German education server Search portal for schools
- PrivatschulBeratung Search for private schools and boarding schools
Do you have any questions?
Let us advise you on your opportunities to work and live in Germany. Our experts will support you with questions regarding job search, visa, recognition and learning German.
You can find out more about the various contact options by clicking on one of the icons in the bar below.


